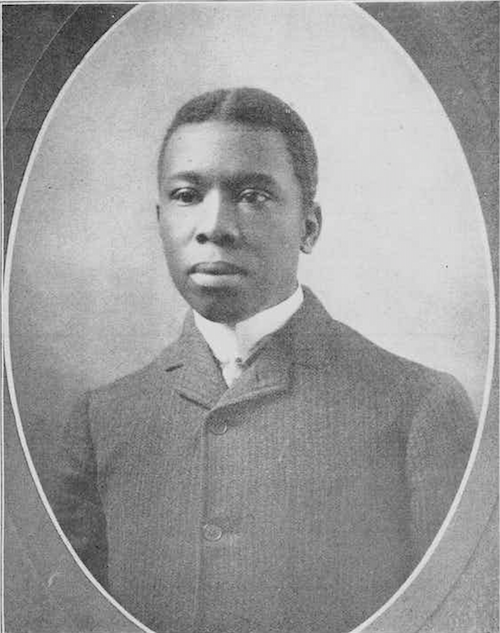
In his short yet prolific life, Dunbar used folk dialect to give voice and dignity to the experience of black Americans at the turn of the 20th century. He was the first Black American to make a living as a writer and was seminal in the start of the New Negro Movement and Harlem Renaissance.
Dunbar also penned one of the most iconic phrases in black literature – “I know why the caged bird sings” – his poem “Sympathy.”
“… When his wing is bruised and his bosom sore, When he beats his bars and he would be free; It is not a carol of joy or glee, But a prayer that he sends from his heart’s deep core, But a plea, that upward to Heaven he flings – I know why the caged bird sings!”
Published in 1899, “Sympathy” inspired acclaimed black writer and activist Maya Angelou to use Dunbar’s line as the title of her seminal autobiography.
But Dunbar’s artistic legacy is often overlooked. This, despite the fact that his work influenced a number of other great African American literary giants, including Langston Hughes, Nikki Giovanni, James Weldon Johnson, Zora Neale Hurston and Margaret Walker.
In a very real sense, Dunbar is your favorite poet’s favorite poet.
A blooming life of writing
Born on June 27, 1872, to two formerly enslaved people from Kentucky, Dunbar was raised by his mother, and they eventually settled in Dayton, Ohio.
While there, Dunbar attended the integrated Dayton Central High School. An exceptional writer, Dunbar was the only black student in his class and became editor-in-chief of the high school newspaper as well as a member of the literary and drama clubs and debating society.
He also became friends with a white classmate who, with his brother, would later invent the airplane – Orville Wright.

The two knew each other well.
Their friendship led to business as the Wright brothers, who owned a printing press, were the first to print Dunbar’s writings, including the newspaper Dunbar started and edited, the Dayton Tattler, the first black newspaper in that city.
After high school, the lives of Dunbar and Wright took different turns.
Unable to find consistent pay for his writing, Dunbar worked a variety of jobs, including as a janitor in one downtown Dayton office building and as an elevator operator in another. Not one to miss a business opportunity, the 20-year-old Dunbar sold his first book of poetry, “Oak and Ivy,” to passengers he met on the elevator.
He found another such job after he moved to Washington, D.C., and worked stacking shelves at the Library of Congress. According to his wife, Alice Dunbar, an accomplished writer in her own right, it was there that her husband began to think about a caged bird.
“… The torrid sun poured its rays down into the courtyard of the library and heated the iron grilling of the book stacks until they were like prison bars in more senses than one,” Dunbar wrote. “The dry dust of the dry books … rasped sharply in his hot throat, and he understood how the bird felt when it beats its wings against its cage.”
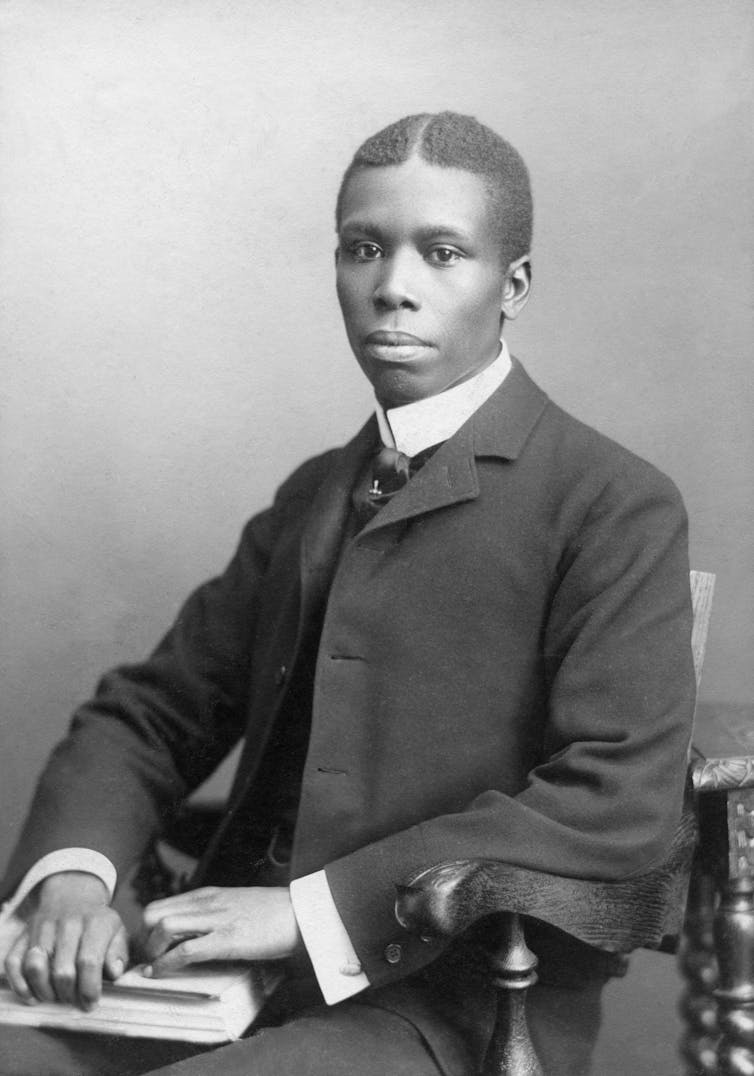

Dunbar’s first break came when he was invited to recite his poems at the 1893 Worlds Fair, where he met Frederick Douglass, the famous abolitionist. Impressed, Douglass gave Dunbar a job and called him the “the most promising young colored man in America.”
Dunbar’s second break came three years later. On his 24th birthday, he received a glowing Harper’s Weekly review of his second book of poetry, “Majors and Minors,” from the prominent Ohio-raised literary critic William Dean Howells.
That review cam with a mixed blessing. Howells’ praise of Dunbar’s use of dialect limited Dunbar’s ability to sell his other styles of writing.
But that same review helped catapult Dunbar to international acclaim.
His stardom didn’t last long, though.
Diagnosed with tuberculosis in 1900, Dunbar died from complications of the disease on Feb. 9, 1906.
But his work survives.
Dunbar’s musical legacy
In all, Dunbar wrote 600 poems, 12 books of poetry, five novels, four volumes of short stories, essays, hundreds of newspaper articles and lyrics for musicals.
His poetry has been continuously set by composers, from his contemporaries to living composers still living today, including Carrie Jacobs Bond, John Carpenter, Harry Thacker Burleigh, William Bolcom and Zenobia Powell Perry.
Florence Price’s numerous settings of his texts include popular and advertisement music, while William Grant Still’s “Afro-American” symphony features spoken epigraphs of Dunbar poems before each movement.

Dunbar’s legacy in apparent not only in the concert hall, but on the theatrical stage as well.
Dunbar was librettist for an operetta by Samuel Coleridge Taylor, “Dream Lovers,” written specifically for Black singers.
Dunbar’s own extraordinary life became the subject for operas as composers Adolphus Hailstork, Richard Thompson, Steven Allen and Jeff Arwady composed works depicting Dunbar’s legacy.
The collaborations of Dunbar and Will Marion Cook produced the first examples of contemporary musical theater.
Without Paul’s contributions with “In Dahomey” and “Jes Lak White Fo'ks,” in my view there would be no “Hamilton,” the modern Broadway musical written by Lin-Manuel Miranda in 2015.
‘We wear the mask’
Dunbar’s works celebrated all of humanity.
He turned the plantation tradition on its head by using dialect to not only offer critical social commentary, as in his poem “When Malindy Sings,” but also to portray oft-ignored humanity, as in “When Dey ‘Listed Colored Soldiers.”
Dunbar’s works provide historical snapshots into the everyday lives of working-class black Americans.
None were as poignant as his poem “We Wear the Mask.”
“We wear the mask that grins and lies, It hides our cheeks and shades our eyes, This debt we pay to human guile; With torn and bleeding hearts we smile, And mouth with myriad subtleties.”
• • •• • •
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.